Gum disease is one of the two most common diseases that affect our oral cavity. This disease is a condition affecting the gum and bone surrounding the teeth. The disease does not produce obvious signs and symptoms until it has progressed to an advanced stage. In all stages of gum disease, patients usually suffer from bleeding gums as a result of bacteria causing damage to the gums.
Gum specialists (Periodontists) are specially trained dentists who can detect and treat the complete range of gum diseases.
What is Gum Disease?
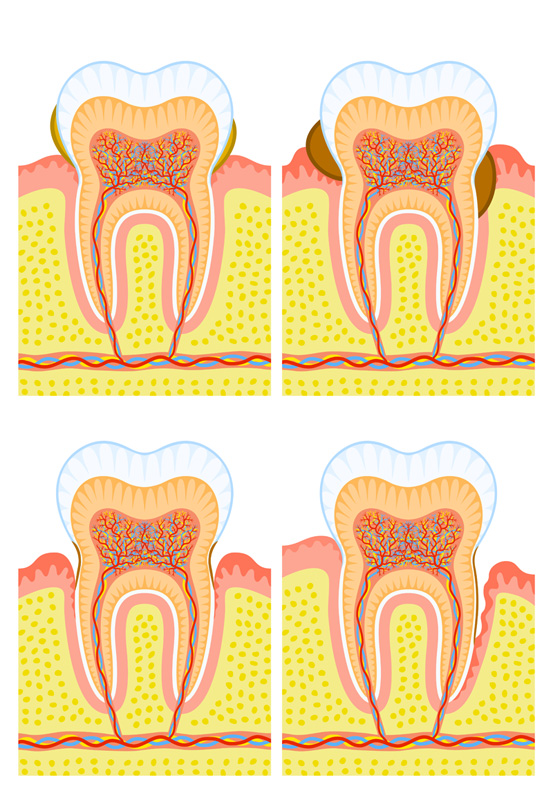
In order to understand gum disease, we need to first understand the structures surrounding the tooth. The tooth is divided into the crown and the root. The root is surrounded by bone, which in turn is covered by gums. There is a space between the tooth and gums, called a pocket, which is present both in healthy and diseased states.
Gum disease originates from bacteria that gain entry into the pocket. When bacteria enter, they attack the gums. This causes injury to the gums, resulting in spontaneous bleeding or upon touching, pain, redness, and sometimes swelling.
If the bacteria harden to form tartar, it can spread deeper towards the bone and cause destruction of the bone and deepening of the periodontal pocket.
In the advanced stage of gum disease (periodontitis), the tooth has lost so much bone that it becomes shaky and may drift out of position. In the late stage of gum disease, the tooth can no longer be kept and has to be extracted.
Bacteria in the gums can enter our blood stream and be transported to the various organs in the body, like the heart, kidneys, womb etc. For example, harmful chemicals produced by the bacteria can increase the insulin resistance of diabetic patients and worsen the diabetic condition. It is also well established by the World Health Organization (WHO) that diabetes can lead to worsening of gum disease.